NPK Fertilizer Production Line: The Core of Modern Crop Nutrition
In the landscape of global agriculture, the efficient and precise delivery of nutrients is paramount. The NPK Fertilizer Production Line stands as a technological cornerstone, transforming raw chemical materials into the uniform, compound granules that fuel high-yield, sustainable farming. It represents a sophisticated fusion of chemical engineering and industrial automation, dedicated to producing the balanced nutrition that modern crops demand.
Core Advantages: Precision, Efficiency, and Uniformity
The NPK production production line moves beyond simple blending, offering integrated advantages that define its role in advanced agriculture:
Unmatched Nutrient Consistency: Through chemical reaction and granulation, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients are homogeneously fused within each granule. This guarantees every particle has an identical nutrient profile, ensuring even field distribution and predictable crop uptake for maximum efficiency.
Engineered Physical Quality: The process yields granules with high crushing strength, excellent roundness, and low dust. This ensures product integrity during bulk handling, storage, and mechanical application, reducing losses and improving farm logistics.
Formula Flexibility & Control: Modern computer-controlled systems allow for precise adjustment of NPK ratios and easy incorporation of secondary nutrients (e.g., calcium, magnesium, sulfur) and micronutrients. This enables the production of customized fertilizers tailored to specific soil conditions, crops, and growth stages.
High-Volume Production Economics: Continuous, automated operation achieves significant scale, driving down unit production costs and making high-quality compound fertilizer accessible for large-scale agricultural use.
Environmental Responsibility: Integrated scrubbing and filtration systems capture dust and recover gases (like ammonia), minimizing emissions and aligning with stringent environmental standards for cleaner manufacturing.
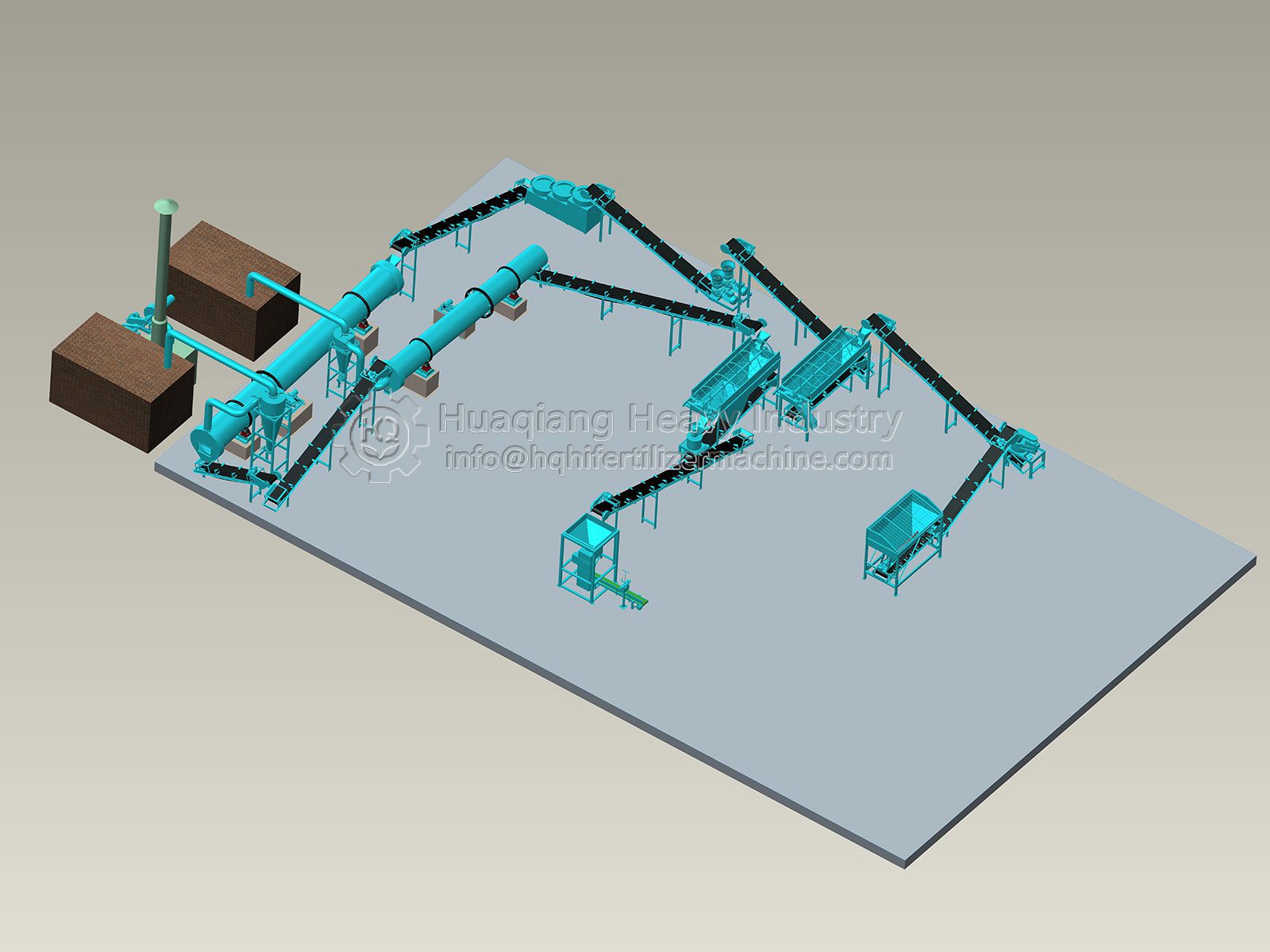
The Production Process: A Continuous Symphony
A modern NPK line is a seamless integration of sequential processes:
Raw Material Preparation & Batching
Key Equipment: Crushers, Screens, Precision Weigh Feeders.
Base materials (urea, MAP, DAP, MOP, etc.) are sized and fed via high-accuracy loss-in-weight or belt feeders. This stage is critical for formula fidelity.
Mixing & Granulation
Key Equipment: Pre-mixers, Rotary Drum Granulator.
Materials are horizontal mixer. The mix enters the granulation drum, where controlled addition of steam and/or acids (e.g., phosphoric acid) creates ideal conditions for chemical reactions and the formation of moist granules via the rolling action.
Drying, Cooling & Sizing
Key Equipment: Rotary Dryer, Cooler, Vibrating Screens.
Granules are dried to achieve final hardness and then cooled to stabilize their structure and prevent caking. Vibrating screens separate on-spec product. Oversized material is crushed, and fines are recycled back to the rotary drum granulator, creating a closed-loop system.
Product Enhancement & Packaging
Key Equipment: Coating Drum, Automated Packaging Line.
Granules may be coated with anti-dust or anti-caking agents. Finally, an automated weighing and bagging system prepares the finished product for palletizing and shipment.
Distinctive Value: Compound vs. Blend
This line produces compound fertilizer, which is fundamentally different from bulk blends (BB fertilizer):
Compound (NPK): Nutrients are chemically combined into each granule. This ensures uniform distribution in the field, eliminates nutrient segregation, and is ideal for broadcasting. It is a premium, consistent product.
Bulk Blend (BB): A physical mix of different granular nutrient sources. While flexible and quick to produce, it carries a risk of particle segregation during handling, which can lead to uneven nutrient application.
Strategic Applications
NPK lines are essential for:
Large-scale fertilizer manufacturers supplying global markets.
Agricultural regions requiring reliable, high-quality base fertilizer products.
Production of specialized fertilizers for specific crops like horticulture, turf, or orchards.
Conclusion
The NPK Compound Fertilizer Production Line is more than machinery; it is the backbone of scientific nutrient management. By delivering precision, consistency, and efficiency at scale, it empowers farmers to meet the world’s growing food demands while optimizing resource use. Investing in this technology is an investment in agricultural productivity, sustainability, and the future of global food security.